
E-mail: font@focusonnature.com
Phone: Toll-free in USA 1-888-721-3555
or 302/529-1876
 |
PO
Box 9021, Wilmington, DE 19809, USA E-mail: font@focusonnature.com Phone: Toll-free in USA 1-888-721-3555 or 302/529-1876 |
 Wildflowers
Wildflowers
and some other plants
of Eastern
North America
in the
Mid-Atlantic
Region
from Pennsylvania and New
Jersey
to North Carolina
Part 2:
by Families alphabetically
from Knotweed
to Yellow-eyed Grass
including plants seen during Focus On Nature Tours
noted with an (*)
during tours thru 2015
in the months of May, June, July, August,
September, October
In this list, there
are some notes relating to MEDICINAL, EDIBLE, & POISONOUS PLANTS.
The compilation of this
two-part list
of Plants of Eastern North America by Armas Hill
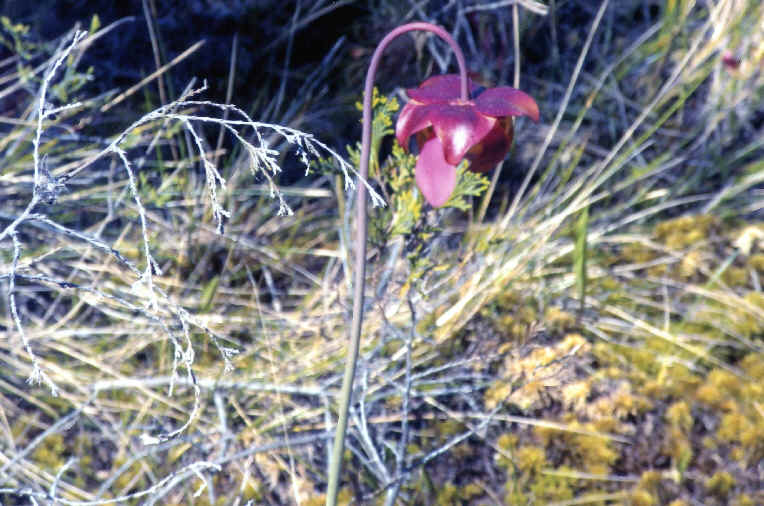
Photo at upper right: ROUND-LEAVED SUNDEW
Among the sources for list here are the books:
"Wildflowers in the Pine Barrens of New Jersey", by Howard
Boyd, published in 2001,
"Wildflowers of Delaware and the Eastern Shore", by Claude
Phillips, published in 1978.
including those in Delaware, and parts of Maryland and
Virginia.
"Wildflowers of Pennsylvania", by Mary Joy Haywood and Phyllis
Monk, published in 2001
"Wildflowers in Color", by Arthur Stupka and Donald Robinson,
published in 1965,
referring to those in the Southern Appalachian Mountains, particularly in the
Shenandoah and Great Smoky National Parks.
More books used as informational sources follow here, after the codes.
Families
below in: Wildflowers and Other Plants of Eastern North
America, Mid-Atlantic, Part 1
Acanthus
Agave Amaranth Aralia (or
Ginseng) Arum (or Calla)
Balsam Barberry
Beech (incl. Oaks) Bellflower (or Bluebell)
Bignonia Birch Bittersweet (or Staff-vine)
Bladderwort (or Birthwort) Bloodwort Bogbean
Bogmoss Borage (or Forget-me-not)
Broomrape Buckthorn
Bunchflower Bur-reed Buttercup (or
Crowfoot) Cactus Caltrop
Camellia (or Tea) Cattail
Custard-apple Cypress Cyrilla
Daisy (or Aster) Diapensia
Dogbane Dogwood Duckweed
Ebony Elm Evening Primrose (or Willow
Herb) Ferns
Fig-marigold (or Carpetweed) Figwort (or
Snapdragon) Flax
Flowering-rush Four o'clock
Fumitory (or Earthsmoke) Gentian
Geranium Gooseberry
Goosefoot Gourd Grape
Greenbriar Heath Hemp
Holly Honeysuckle
Hydrangea Hypoxis (or Daffodil) Iris
Among the Plant
Families here in part 2 of this list, links to these:
Knotweed (or Dock, Buckwhat, Swartweed) Laurel Legume (or Pea)
Lichen Lily
Lizard's-tail Logania Loosestrife
Lopseed Lotus Madder
Magnolia Mallow
Meadow-beauty Milkweed
Milkwort Mint
Moonseed Morning Glory
Mulberry Mustard
Nettle Nightshade (or Potato) Olive Orchid
Palm Parnassus-grass Parsley
(or Celery)
Passionflower Phlox (or Polemonium) Pickerelweed (or Water Hyacinth)
Pine Pineapple
Pink (or Carnation) Pipewort Pitcher-plant Plantain
Plumbago (or Sea
Lavender)
Pokeweed Pondweed
Poppy Primrose Purslane Rockrose Rose
Rue
(or Citrus) Rush
Sandalwood (with Mistletoe) Saxifrage
Sedge Soapberry
(incl. Maples) Spiderwort Spurge
St John's Wort Stonecrop
Storax Sumac (or Cashew)
Sundew Sweetleaf Sweetshrub
Sycamore Teasel Valerian Vervain Violet Walnut Waterleaf Water-lily Water-milfoil
Water-plantain Wax-myrtle
White Alder Willow
Witch-hazel Wood-sorrel Yam
AN ALPHABETICAL DIRECTORY OF PLANT GENERA IN THIS WEBSITE NOTING FAMILIES
Additional Links:
Upcoming
FONT Birding & Nature Tours in:
North Carolina, and Delaware, Maryland & Virginia
Elsewhere
In this website, Other Lists & Photo Galleries of Eastern North American:
Butterflies Moths Dragonflies & Damselflies Amphibians & Reptiles Mammals
A List & Photo Gallery of North American Birds, in 6 parts
North Carolina Birds
In this website, Other Lists & Photo Galleries
relating to Plants:
Desert Plants of the Southwest US & northern Mexico
Northern Plants in Alaska, Iceland, and Hokkaido, Japan
Plants of the West Indies Fruiting Plants and Others in Brazil Wild Orchids of the Americas
Other Photo Galleries of Plants Directory of Photos in this Website
HERE'S A LINK TO CHAD KREMP'S WEBSITE RELATING TO POISONOUS PLANTS:
http://www.kremp.com/the-hikers-guide-to-poisonous-plants-articles.htm
![]()
Codes:
DP: Delmarva Peninsula
(including Delaware and parts of Maryland and Virginia)
NJ: New Jersey, including in southern New Jersey,
the Pine Barrens
PA: Pennsylvania
SA: southern Appalachians (including in
Shenandoah National Park in Virginia and
the Great Smoky Mountains National
Park in North Carolina)
(ph): species with a photo or drawing in the FONT website
Numbers noted as (NA:xx)
refer to photo numbers in the "National Audubon Society Field Guide to
North American Wildflowers, Eastern Region" - Revised Edition
(2001) Revising author: John Thierer. Original author: William Niering.
Numbers noted as (NW:xx)
refer to pages with photos in the "National Wildlife Federation Field
Guide to Wildflowers of North America" by David Brandenburg, 2010.
Numbers noted as
(SP:xx)
refer to the numbers of
the photos in
"The Smithsonian Guide to Seaside Plants of the Gulf and
Atlantic Coasts"
by Wilbur and Marion Duncan, 1987.
Numbers noted as (ST:xx) refer to the page
with an illustration in "The Sibley Guide to Trees" by David A.
Sibley, 2009.
Numbers noted as (WP:xx) refer to the page
with a photograph in the book "Wildflowers of Pennsylvania" by
Mary Joy Haywood & Phyllis Monk, 2001. Overall, the photographs in that book
are excellent.
An enjoyable and informative book to read is "Wild Plants of America: A
Select Guide for the Naturalist and Traveler" by Richard M. Smith,
1989.
Among the places covered in the book, also included in the scope of this list,
are the New Jersey Pine Barrens, the Southern Appalachians, the pinelands of
North Carolina, and coastal North Carolina.
Some of the interesting information in the book has been incorporated into this
list. Line drawings in the list are from that book.
Another good book, filled with info and used here as a source, is "The
Backyard Wilderness, from the Canadian Maritimes to the Florida Keys",
by Vincent Abraitys, 1975.
A historical book, good as a reference, is "The Plants of Southern New
Jersey: Report of the New Jersey State Museum Part 2", by Witmer Stone,
1911.
Among sources for info given here relating to the host plants of butterflies and
moths are:
"Butterflies of the East Coast, an Observer's Guide", by Rick
Cech and Guy Tudor, 2005, and
the "Peterson Field Guide to Moths of Northeastern North America"
by David Beadle and Seabrook Leckie, 2012.
The book "Wild America" by Roger Tory Peterson and James
Fisher, 1955 is also referred to in this list.
And yet another fine book has been a good source of information: "The
Appalachians" by Maurice Brooks, 1965.
Part 2 of a List of Wildflowers & some Other Plants
of Eastern North America in the Mid-Atlantic Region:
Knotweed to Yellow-eyed Grass
Knotweed, Smartweed, or
Buckwheat, or Dock Family,
ACANTHACEAE































![]()